If you notice this while reconciling your bank accounts, you can take measures to halt the fraud and recover your money. This is a simple data entry error that occurs when two digits are accidentally reversed (transposed) when posting a transaction. For example, you wrote a check for $32, but you recorded it as $23 in your accounting software. A bank reconciliation statement is only a statement prepared to stay abreast with the bank statement; it is not in itself an accounting record, nor is it part of the double entry system. The bank statement submitted by the businessman at the end of May will not contain an entry for the check, whereas the cash book will have the entry.
Bank Reconciliation Statement
- For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing.
- Companies prepare bank reconciliation statements as a comprehensive accounting comparison tool.
- You should perform bank reconciliation at least every month—which is how often your bank sends a bank statement.
- 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
To be effective, a bank reconciliation statement should include all transactions that impact a company’s financial accounts. During the bank reconciliation process, you’ll compare your bank statements to your business’s financial records. You’ll note any differences between your business’s cash records and your bank’s records, then adjust your internal records to ensure their accuracy. At the end of the process, both your bank account and general ledger (GL) should match, and any differences between the two records should be resolved (or reconciled).
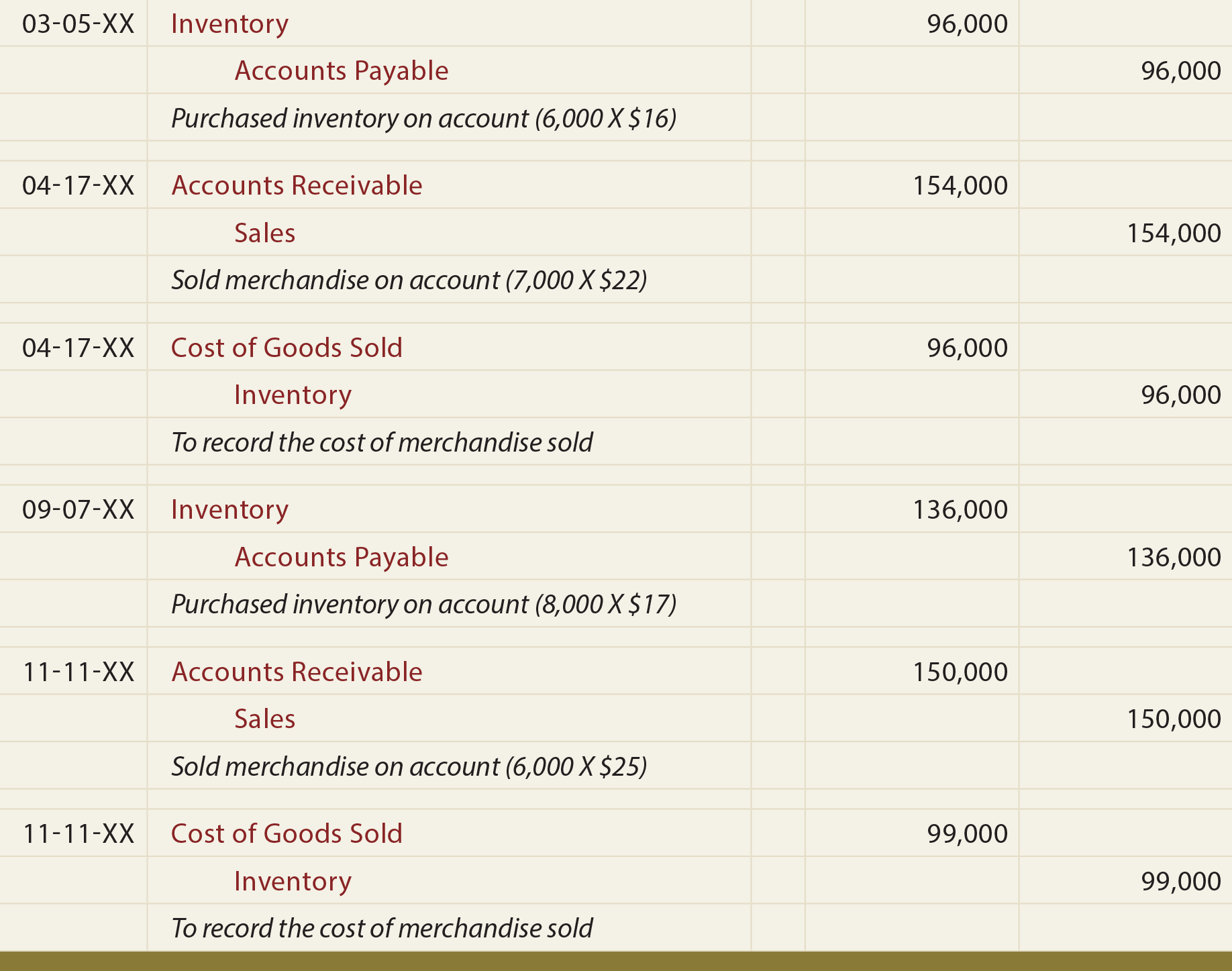
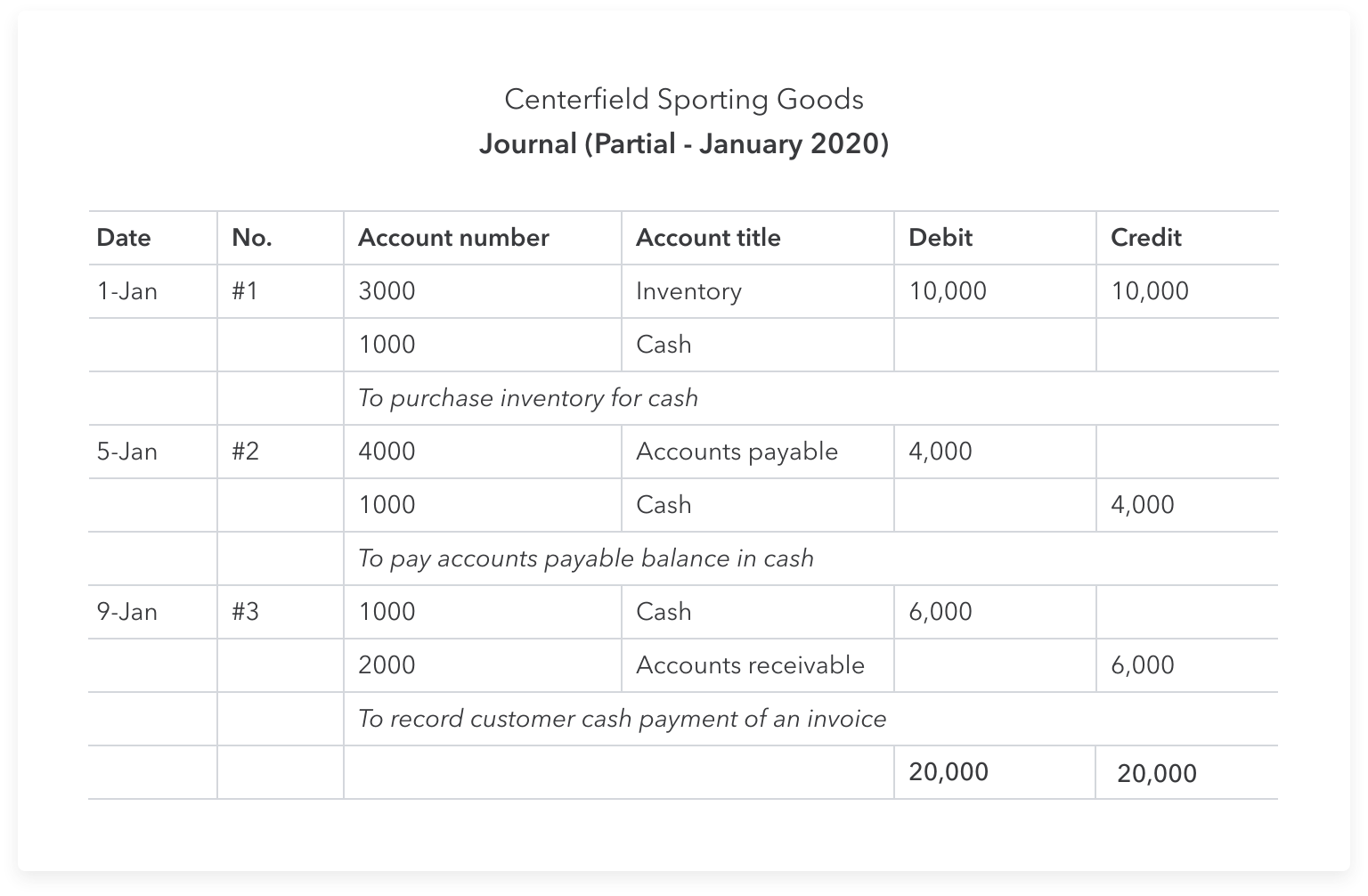
An online template can help guide you, but a simple spreadsheet is just as effective. Throughout the course of business, Fender writes checks to vendors for goods and services. These checks are recorded as expenses (cash out) in Fender’s accounting system as soon as the checks are written. Fender also receives checks from customers and dealers who are buying their guitars. These checks are recorded as income (cash in) as soon as the checks are received.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
This includes payments by customers to your company and payments from your company to employees, contractors, and other goods and services providers. Greg adds the $11,500 of deposits in transit to marginal revenue definition example and formula his bank statement balance, bringing him to $99,500. He also subtracts the $500 in bank fees from his financial statement balance, bringing him to $99,500 and balancing the two accounts. When done frequently, reconciliation statements help companies identify cash flow errors, present accurate information to investors, and plan and pay taxes correctly.
Performing regular bank reconciliations helps you stay on top of cash flow, keep organized records for tax season, and minimize the risk of fraud and theft. Add the amount of deposits in transit and subtract the amount of any outstanding checks from your bank statement’s cash balance to arrive at (and record) an adjusted bank balance. Similarly, add any interest payments or bank fees to your business’s cash accounts to find your adjusted cash balance. Hopefully, once you’ve dealt with deposits in transit, outstanding checks, interest payments, and bank fees, your bank statement and internal accounting records will match. Resolving the issue could mean paying a bill, depositing a check, or entering a forgotten transaction into your general ledger.
Do you own a business?
One of the most common causes of discrepancies in bank reconciliations is delays in deposit and transaction processing. Checks sent or received at the end of the day, or toward the end of the month, may be subject to delay which will prevent them from being included on the bank statement. Accounting for these delays is key to reconciling the total amounts on the company’s financial statement and the bank statement. Begin with a side-by-side comparison of your bank account statement and your company’s accounting records. Check that your financial transaction records include all payments and deposits for the transaction period, as well as the final balance. You’ll need a few items to perform a bank reconciliation, including your bank statement, internal accounting records, and a record of any pending cash transactions (either inflows or outflows).
Identify Discrepancies
All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own.